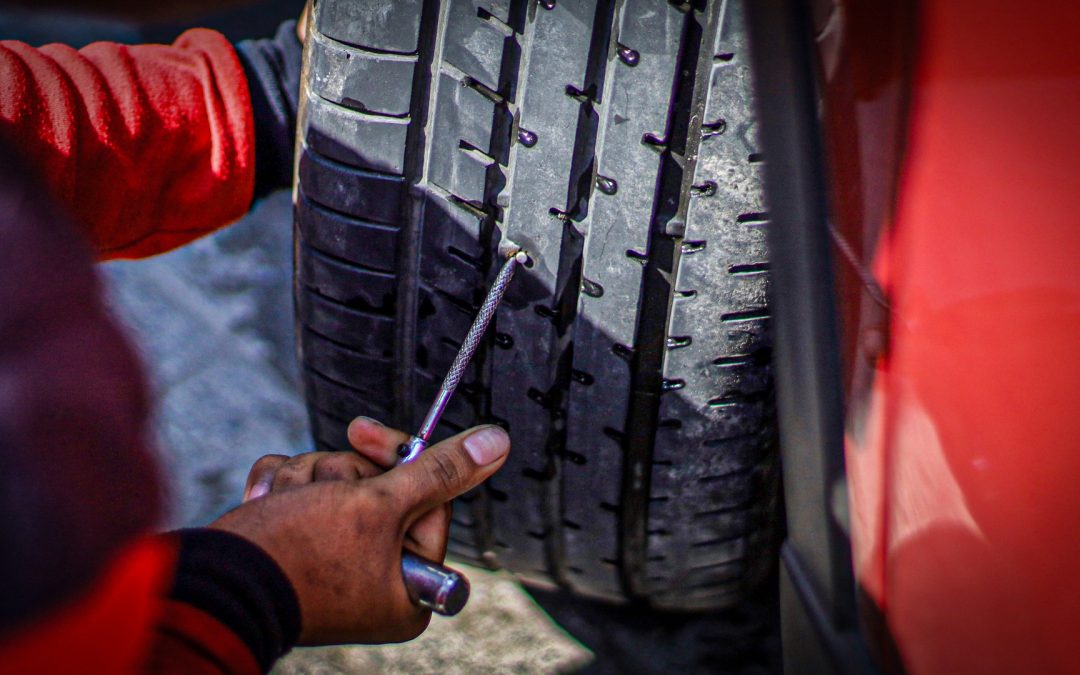
Patching a punctured tire is a common job, but are you up to date on the latest guidance for safe plug locations?

Have you performed a mechanical valve cleaning lately?
Did you ever stop to think about how strange it is we need to do that again, when “decoking” stopped being a necessity half a century ago? Have we outfoxed ourselves in the eternal automotive quest for higher power while simultaneously lowering emissions? When you consider a few of the factors involved in modern emissions abatement, the rather antiquated outcome of mechanical valve cleaning starts to seem like a predictable predicament. So what brought us here?
The first and likely most obvious cause for these valve cleanings is the prevalence of gasoline direct injection (GDI), the process by which fuel is put right into the combustion chamber, not the manifold. The system comes with downsides: Without fuel washing over the back side of the engine’s poppet valves, oil that comes in contact quickly “cooks” and eventually turns into a hard carbon deposit, which needs to be removed mechanically or chemically.
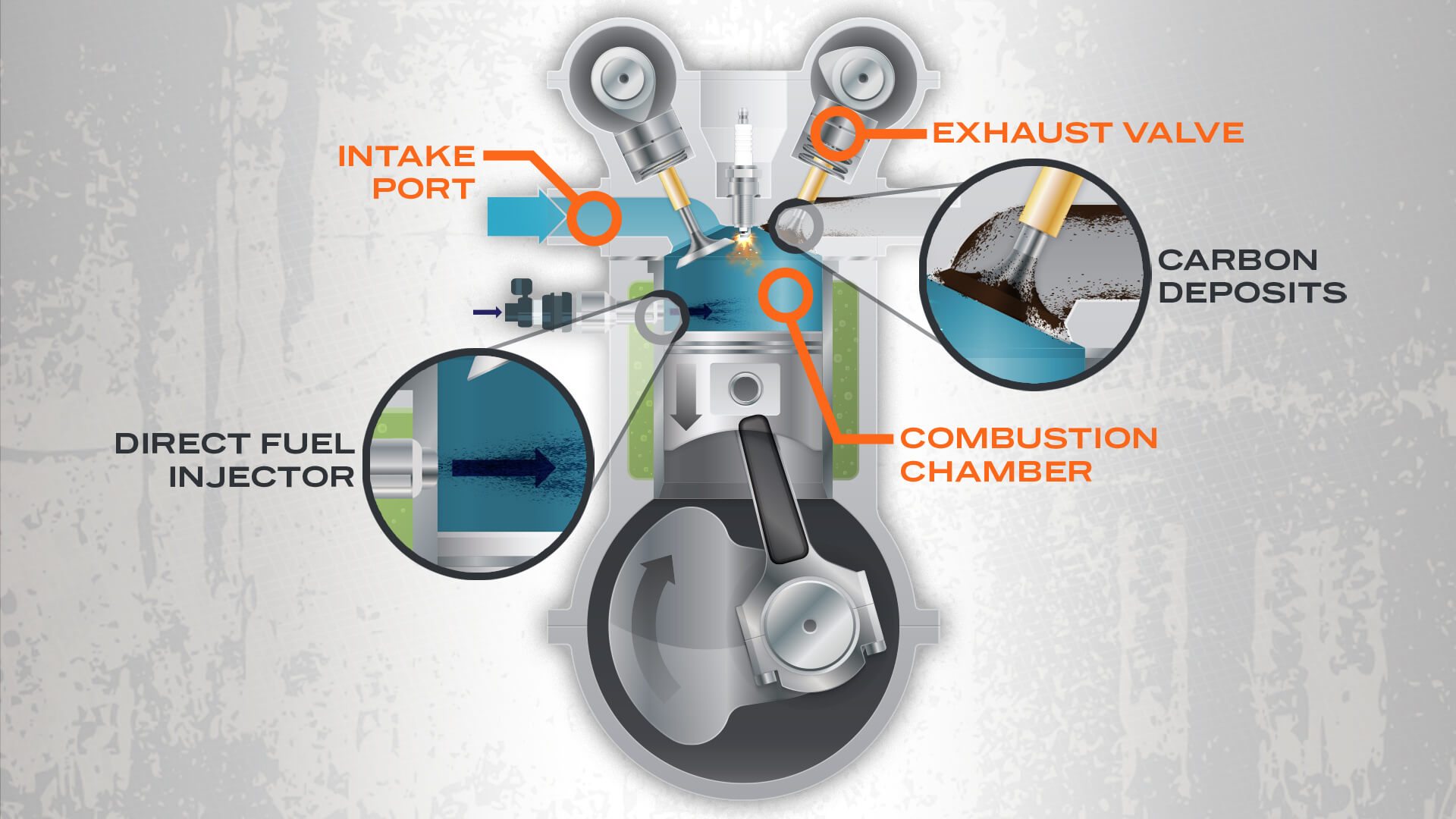
Without fuel to wash the backs of the intake valves, removal of carbon deposits must be performed occasionally through chemical or manual means. Illustration by Josh Seasholtz.
GDI has become prevalent because engine operation at exceedingly lean mixtures becomes possible. Given the incredibly high pressures, fuel is atomized better and the injector can actually be fired multiple times in the combustion cycle. Coupled with other technologies, automakers get the benefit of reduced emissions, greater power, or in some cases, both.
But there are a few other technologies kicking around that make this problem worse.

Once the domain of tuner cars, turbochargers can be found on even the most modest, economy-focused cars in the market today. Photo by Mike Apice.
One is the proliferation of forced induction. Seemingly everything has a turbocharger on it nowadays. According to Wards Auto, nearly 28% of cars and light trucks built in the US in 2017, and that number is on the rise. Once reserved for diesels and exotic, performance gas motors, snails can be found on even basic grocery-getters. Turbochargers generally increase the amount of blow-by gas formed, thus pressurizing the PCV system even more and sending more oil down the valve stems.
Almost comically, this has occurred alongside the proliferation of low tension piston rings. Low tension rings were developed to decrease internal friction losses. According to Federal-Mogul, rings account for 4% of the total friction loss in a gasoline engine. The lower tension does indeed reduce friction losses, but they also allow more blow-by since they are not able to seal the cylinder wall as effectively.
But wait, there’s more. In that same vein of decreasing friction, engine oil viscosity has fallen quite a bit. You’ve likely seen 0W20 and now even 0W16 oils on the auto parts store shelf, whereas the 10W40 you may have run years ago is disappearing. What does this mean? Well…more blow-by. Thinner oil allows more blow-by, further exacerbating this situation.
It’s not all bad, though. Many manufacturers are beginning to incorporate multiple injectors per cylinder—one direct, one indirect. This has the benefit of allowing more fuel at high RPMs, since pulse width can become too short at high speed operation. It also conveniently keeps the backs of the valves clean!

Coking is not a new issue for diesels, either, many of which also are directly injected. Photo by Mike Apice.
These technologies do indeed reduce emissions and friction losses. However, increased oil in the combustion chamber does lead to greater particulate matter (ash) being produced (among a few other items), so it’s not just a net gain; there is a downside to all this residual oil that makes its way into the combustion chamber.
Some of your customers would likely find the cost of this additional “decoking” maintenance a fair price to pay for decreased emissions, and others would not. Irrespective of that fact, scraping crud off poppet valves is once again a fact of mechanical life.
The articles and other content contained on this site may contain links to third party websites. By clicking them, you consent to Dorman’s Website Use Agreement.
Participation in this forum is subject to Dorman’s Website Terms & Conditions. Please read our Comment Policy before commenting.
Description With dozens of electronic control units on automobiles built in the last 25 years, incidents of battery...
Diagnosing an illuminated check engine light (CEL) is something professional technicians do on an everyday basis. The...
Description Patching a punctured tire is a common job, but are you up to date on the latest guidance for safe plug...